What is eFRS?
eFRS stands for Enhanced Financial Reporting System. It is a system used by the DepED for recording various financial data and consequently generating reports as required by oversight agencies such as the COA and DBM.
Why do we need to use eFRS?
eFRS stands for Enhanced Financial Reporting System. It is a system used by the DepED for recording various financial data and consequently generating reports as required by oversight agencies such as the COA and DBM.
Why do we need to use eFRS?
The current version of eFRS incorporates UACS as mandated by COA-DBM-DOF Joint Circular No. 2013-1. With the 54 digit format of UACS, DepEd realized the difficulty in properly coding each financial transaction to its appropriate UACS code. Although this would be addressed with the advent of GIFMIS, which will come in late 2015, there is still a gap of approximately 2 years from the implementation of UACS to that of GIFMIS. As such, there is a need to have a system to support DepEd during this gap. Hence, the adoption of the enhanced FRS.
Background
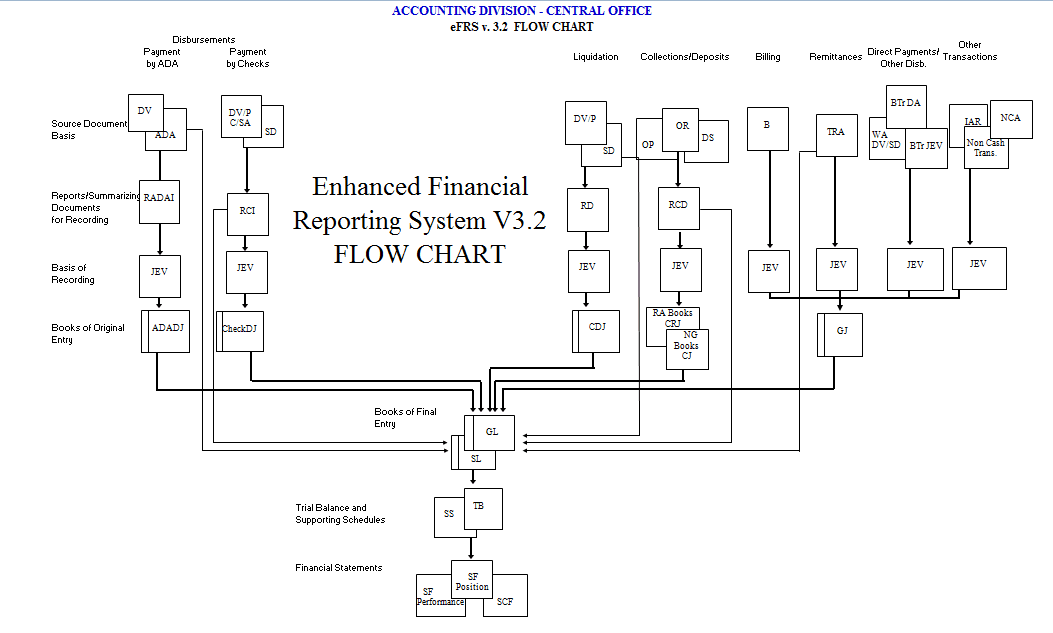
The Enhanced Financial Reporting System (eFRS) originated from the basic Financial Reporting System (FRS) used by some accounting units in the Department of Education (DepED). It was initiated by central office a few years back and its development was then continued by Mr. Harold Magadia, a programmer in the Accounting Division of DepEd Central Office, up until its latest version. The current version of eFRS is 3.1 or the eFRS V3.1. Hence, all eFRS term used in this manual refers to eFRS V3.1.
The principal developer of eFRS is Mr. Magadia himself together with the guidance and supervision of the Accountants from DepED Central Office. Feedbacks from field offices were also incorporated in the system along with the recommendations and suggestions pointed out by the consulting team. The main distinction of eFRS as compared to its predecessors is that it is already Unified Account Code Structure (UACS) compliant. This means that it can already cater the 46-digit UACS code, as mandated through COA-DBM-DOF Joint Circular No. 2013-1, in recording financial transaction. In addition, the eFRS adheres to relevant rules and regulations as mandated by the Commission on Audit (COA) and the Department of Budget and Management (DBM), including strict compliance to pertinent guidelines and issuances deemed necessary by these oversight agencies.
The main purpose of eFRS is to provide relative ease in recording transactional data needed for accounting units as compared to the manual process or even with standard spreadsheets especially when coding the 46-digit UACS code. It was also designed to produce appropriate reports and export relevant financial data as needed. Generally, eFRS is designed to provide support for Accounting personnel in the meantime while the Government Integrated Financial Management Information System (GIFMIS) is still undergoing development. Until such time when GIFMIS will be fully implemented in DepED, eFRS will play a vital role in recording accounting entries and other financial data as well as generating reports and other financial statements.
Background
The Enhanced Financial Reporting System (eFRS) originated from the basic Financial Reporting System (FRS) used by some accounting units in the Department of Education (DepED). It was initiated by central office a few years back and its development was then continued by Mr. Harold Magadia, a programmer in the Accounting Division of DepEd Central Office, up until its latest version. The current version of eFRS is 3.1 or the eFRS V3.1. Hence, all eFRS term used in this manual refers to eFRS V3.1.
The principal developer of eFRS is Mr. Magadia himself together with the guidance and supervision of the Accountants from DepED Central Office. Feedbacks from field offices were also incorporated in the system along with the recommendations and suggestions pointed out by the consulting team. The main distinction of eFRS as compared to its predecessors is that it is already Unified Account Code Structure (UACS) compliant. This means that it can already cater the 46-digit UACS code, as mandated through COA-DBM-DOF Joint Circular No. 2013-1, in recording financial transaction. In addition, the eFRS adheres to relevant rules and regulations as mandated by the Commission on Audit (COA) and the Department of Budget and Management (DBM), including strict compliance to pertinent guidelines and issuances deemed necessary by these oversight agencies.
The main purpose of eFRS is to provide relative ease in recording transactional data needed for accounting units as compared to the manual process or even with standard spreadsheets especially when coding the 46-digit UACS code. It was also designed to produce appropriate reports and export relevant financial data as needed. Generally, eFRS is designed to provide support for Accounting personnel in the meantime while the Government Integrated Financial Management Information System (GIFMIS) is still undergoing development. Until such time when GIFMIS will be fully implemented in DepED, eFRS will play a vital role in recording accounting entries and other financial data as well as generating reports and other financial statements.
Please Download here...................................
eFRS System Manual v1.1.0 (Revised)
FREQUENTLY ASK QUESTIONS
1. Why include MFO/PAP Codes? eFRS is redesigned to comply with UACS, which we otherwise called FOLMO. The new 5-segment and 54-digit code includes the MFO/PAP Codes; without it, the transaction details will be incomplete.
To clarify the use of MFO/PAP Codes, these codes all originate from the approved Budget. Make sure that your copy has standard codes as that of the DepED CO. All your budget items must have corresponding codes. The supporting document as basis for recording is the OBr. Now, the purpose of MFO/PAP Codes is to automatically compare the budgetary expenditures and the accounting expenditures. Thus, only expenses (PS, MOOE, and CO) have MFO/PAP Codes; all other real accounts plus the incomes and non-cash expenses accounts have no required MFO/PAP Codes. Just choose the None or 000000000000000 (15 zeroes).
Further and more comprehensive discussions on MFO/PAP Codes can be read from the attached eFRS User Manual Volume II.
To clarify the use of MFO/PAP Codes, these codes all originate from the approved Budget. Make sure that your copy has standard codes as that of the DepED CO. All your budget items must have corresponding codes. The supporting document as basis for recording is the OBr. Now, the purpose of MFO/PAP Codes is to automatically compare the budgetary expenditures and the accounting expenditures. Thus, only expenses (PS, MOOE, and CO) have MFO/PAP Codes; all other real accounts plus the incomes and non-cash expenses accounts have no required MFO/PAP Codes. Just choose the None or 000000000000000 (15 zeroes).
Further and more comprehensive discussions on MFO/PAP Codes can be read from the attached eFRS User Manual Volume II.
2. What should be the basic Data Entry Discipline? eFRS is a database, intended to capture financial information once but can be used many times. That is one reason why plenty of required input cells. Now, data entry discipline is highly necessary which are:
a. 1 DV is 1 JEV (including ADA disbursements where 1 ADA has many DVs)
b. 1 Check is 1 JEV (in case 1DV has many cheques)
c. 1 Fund Source is 1 JEV (example the payroll where RLIP has a different source)
d. 1 RCD is 1 JEV for collection and 1 JEV for deposit
e. Entry is per check in order to reuse the info in bank recon
f. Entry is per OR or Dep Slip in order to reuse the info in cash management
For LDDAP-ADA with several payees, recording must follow the discipline 1 DV = 1 JEV and must input repeatedly the ADA number.
3. How to establish Subsidiary Ledger? Setting up balances for SLs may be done in a workaround manner. In establishing the SL, set up first the beginning balances using the beginning balance template (in the System Setup menu) of the eFRS. Then proceed to Add/Create Data button, click Other Transactions and prepare journal entries for the SLs; debit/credit thereafter the GL account you established in the setup (as if reversing the accounting entry made). Print the JEV and manually add the SL names and codes. Do the same for the SLs of Cash-LCCA. Only that in the Add/Create Data button, choose Bank Deposits and input the different bank account numbers.
You may find the same instructions in the eFRS User Manual Volume II, attached herewith. The SL for Cash-LCCA is highlighted in the manual with separate instruction for its establishment.
4. The beginning balances of Receivables (including Cash Advances) and Payables accounts for use in the Aging Schedules are not directly captured in the eFRS.
Best thing you can do is use the aging produced by eFRS (for the current year) and then add/minus the beginning balances manually.
Though you can also establish firsthand the SL names and codes in the setting up of Payee List. Say for example, set up BIR-1%, BIR-2%, BIR-3%, BIR-5%, BIR-2316. You shall have 5 payees for BIR in the list. Then every time a transaction with BIR occurs, use the specific payee according to SL.
Take note that JEV for beginning balance established can be edited in the Edit Data facility of the eFRS.
5. How to use the SU’s MOOE Liquidation transaction button? The SU's MOOE Liquidation is specifically included as major transaction type and major transaction button purposely to monitor liquidations of MOOE downloading for every Spending Unit (SU). This is for the use of DOs and Main Campus-IUs which download MOOE to schools under them.
You have to put into the Payee field the concerned School (Elementary and High Schools). Then click and select the Organization Code of the SU in the drop down list. Choose DO for ES and HS without assigned Org Code (Main Campus’ for IUs), or the corresponding Org Code for those HS provided in UACS.
6. A latest version of eFRS is now available, incorporated therein the additional Chart of Accounts as well as those renamed or converted accounts and revised FS Format.
The PPA will no longer be in use as per UACS and revised Chart of Accounts. The Government Equity account also is now renamed “Accumulated Surplus/(Deficit). Under of COA Circular No. 2015-02 dated March 9, 2015, the Financial Statement is become compliant to PPSAS
7. What to do when JEV Number skips or spoils? As regard the skipping or spoilage of JEV numbers, only technicians most importantly the developer, Mr. Harold Magadia, can remedy that. In case you cannot wait Mr. Magadia, you may consider doing the following options:
a. Always take note of the JEV count. What triggers the counting or assigning of new JEV number are clicking the username, identifying the year or month or transaction date in the JEV Number panel, choosing the Transaction Types. When not sure to continue the JEV preparation, never touch the above buttons and fields.
Whenever the new JEV Number is given, please continue encoding and then post transaction. This is to reserve that JEV number for the transaction you supposed to record. Then when you make up your mind, go to Edit Data and search for that JEV Number and edit/finalize the correct JEV.
b. In case that the JEV Number was indeed skipped and spoiled, print a blank JEV, number it according to the lost JEV, and then mark or stamp Cancelled.
8. How to review the number of JEVs you already prepared does not reveal in the Edit Data.
Used the F5 function to refresh the computer unit. That is to let our computer units absorb the information or refresh.
9. How to check or review whether the recording and posting of transactions are correct? The Detailed Trial Balance will help you out. It may not be part of the Financial Reports you’ve been submitting to oversight agencies, but such report will let you know whether the FOLMO is correct.
a. Review the Fund Source Codes whether they are correctly chosen per Account (or Object) Code.
b. Check whether the MFO/PAP Codes are consistent with codes in the Approved Budget.
c. Identify those Account (Object) Codes without Account Titles or Names because that signifies erroneous entry. Such will compromise your GL and SL balances because the GL Code cannot be identified correctly.
10. Whom to seek help and/or technical assistance? The Information Technology/Research Section (ITRS) that will administer a helpdesk for eFRS. You may also email Mr. Harold Magadia at deped.harold@gmail.com or join to the eFRS User Ako at FB Group.
a. 1 DV is 1 JEV (including ADA disbursements where 1 ADA has many DVs)
b. 1 Check is 1 JEV (in case 1DV has many cheques)
c. 1 Fund Source is 1 JEV (example the payroll where RLIP has a different source)
d. 1 RCD is 1 JEV for collection and 1 JEV for deposit
e. Entry is per check in order to reuse the info in bank recon
f. Entry is per OR or Dep Slip in order to reuse the info in cash management
For LDDAP-ADA with several payees, recording must follow the discipline 1 DV = 1 JEV and must input repeatedly the ADA number.
3. How to establish Subsidiary Ledger? Setting up balances for SLs may be done in a workaround manner. In establishing the SL, set up first the beginning balances using the beginning balance template (in the System Setup menu) of the eFRS. Then proceed to Add/Create Data button, click Other Transactions and prepare journal entries for the SLs; debit/credit thereafter the GL account you established in the setup (as if reversing the accounting entry made). Print the JEV and manually add the SL names and codes. Do the same for the SLs of Cash-LCCA. Only that in the Add/Create Data button, choose Bank Deposits and input the different bank account numbers.
You may find the same instructions in the eFRS User Manual Volume II, attached herewith. The SL for Cash-LCCA is highlighted in the manual with separate instruction for its establishment.
4. The beginning balances of Receivables (including Cash Advances) and Payables accounts for use in the Aging Schedules are not directly captured in the eFRS.
Best thing you can do is use the aging produced by eFRS (for the current year) and then add/minus the beginning balances manually.
Though you can also establish firsthand the SL names and codes in the setting up of Payee List. Say for example, set up BIR-1%, BIR-2%, BIR-3%, BIR-5%, BIR-2316. You shall have 5 payees for BIR in the list. Then every time a transaction with BIR occurs, use the specific payee according to SL.
Take note that JEV for beginning balance established can be edited in the Edit Data facility of the eFRS.
5. How to use the SU’s MOOE Liquidation transaction button? The SU's MOOE Liquidation is specifically included as major transaction type and major transaction button purposely to monitor liquidations of MOOE downloading for every Spending Unit (SU). This is for the use of DOs and Main Campus-IUs which download MOOE to schools under them.
You have to put into the Payee field the concerned School (Elementary and High Schools). Then click and select the Organization Code of the SU in the drop down list. Choose DO for ES and HS without assigned Org Code (Main Campus’ for IUs), or the corresponding Org Code for those HS provided in UACS.
6. A latest version of eFRS is now available, incorporated therein the additional Chart of Accounts as well as those renamed or converted accounts and revised FS Format.
The PPA will no longer be in use as per UACS and revised Chart of Accounts. The Government Equity account also is now renamed “Accumulated Surplus/(Deficit). Under of COA Circular No. 2015-02 dated March 9, 2015, the Financial Statement is become compliant to PPSAS
7. What to do when JEV Number skips or spoils? As regard the skipping or spoilage of JEV numbers, only technicians most importantly the developer, Mr. Harold Magadia, can remedy that. In case you cannot wait Mr. Magadia, you may consider doing the following options:
a. Always take note of the JEV count. What triggers the counting or assigning of new JEV number are clicking the username, identifying the year or month or transaction date in the JEV Number panel, choosing the Transaction Types. When not sure to continue the JEV preparation, never touch the above buttons and fields.
Whenever the new JEV Number is given, please continue encoding and then post transaction. This is to reserve that JEV number for the transaction you supposed to record. Then when you make up your mind, go to Edit Data and search for that JEV Number and edit/finalize the correct JEV.
b. In case that the JEV Number was indeed skipped and spoiled, print a blank JEV, number it according to the lost JEV, and then mark or stamp Cancelled.
8. How to review the number of JEVs you already prepared does not reveal in the Edit Data.
Used the F5 function to refresh the computer unit. That is to let our computer units absorb the information or refresh.
9. How to check or review whether the recording and posting of transactions are correct? The Detailed Trial Balance will help you out. It may not be part of the Financial Reports you’ve been submitting to oversight agencies, but such report will let you know whether the FOLMO is correct.
a. Review the Fund Source Codes whether they are correctly chosen per Account (or Object) Code.
b. Check whether the MFO/PAP Codes are consistent with codes in the Approved Budget.
c. Identify those Account (Object) Codes without Account Titles or Names because that signifies erroneous entry. Such will compromise your GL and SL balances because the GL Code cannot be identified correctly.
10. Whom to seek help and/or technical assistance? The Information Technology/Research Section (ITRS) that will administer a helpdesk for eFRS. You may also email Mr. Harold Magadia at deped.harold@gmail.com or join to the eFRS User Ako at FB Group.


